Understanding Asthma: Symptoms, Triggers, and Management
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, asthma can make breathing difficult and impact daily activities if not well-managed. Whether you’ve been diagnosed with asthma or want to learn more about it, this post offers a comprehensive overview of what asthma is, its causes, symptoms, and how to manage it effectively.
What Is Asthma?
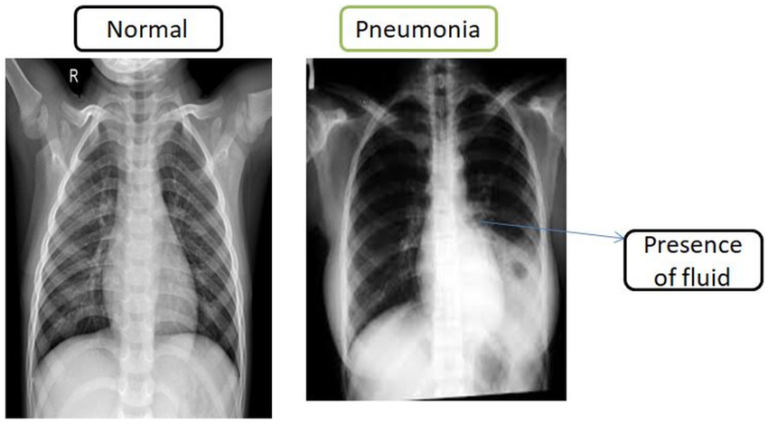
Asthma is a long-term condition in which the airways in the lungs become inflamed and narrow, producing extra mucus. This leads to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. The severity of asthma varies from person to person — for some, it’s a minor inconvenience, while for others, it can be life-threatening.
Common Symptoms of Asthma
Asthma symptoms can range from mild to severe and may worsen during physical activity, at night, or in response to allergens. Common symptoms include:
- Wheezing (a whistling sound when breathing)
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness or pressure
- Coughing, especially at night or early morning
- Difficulty sleeping due to breathing issues
What Triggers Asthma Attacks?
Asthma triggers are substances or conditions that cause the airways to react. Understanding and avoiding your triggers is essential for effective asthma control. Common triggers include:
- Allergens: Pollen, dust mites, pet dander, mold
- Air irritants: Smoke, pollution, chemical fumes
- Respiratory infections: Colds, flu, or sinus infections
- Physical activity: Especially in cold, dry air (exercise-induced asthma)
- Weather: Sudden changes in temperature or humidity
- Strong emotions or stress
- Certain medications: Like aspirin or beta-blockers
Types of Asthma
- Allergic Asthma – Triggered by allergens like dust or pollen
- Non-Allergic Asthma – Triggered by stress, cold air, or infections
- Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction (EIB) – Brought on by physical activity
- Occupational Asthma – Triggered by workplace irritants
- Childhood Asthma – Affects children and can improve or persist into adulthood
Managing and Treating Asthma
While there’s no cure for asthma, it can be effectively managed with medication and lifestyle changes.
Medications
- Quick-relief inhalers (bronchodilators): For fast symptom relief during an asthma attack
- Long-term control medications: Inhaled corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, and long-acting bronchodilators help reduce inflammation and prevent symptoms
- Biologics: Advanced treatments for severe asthma
Self-Care and Lifestyle Tips
- Identify and avoid your triggers
- Use a peak flow meter to monitor lung function
- Follow your asthma action plan created by your doctor
- Keep your environment clean and allergen-free
- Get vaccinated against respiratory infections like the flu
When to See a Doctor
You should see a doctor if:
- You have frequent asthma symptoms or need your inhaler more than twice a week
- Your symptoms are getting worse
- You experience nighttime awakenings due to asthma
- You have a severe asthma attack that doesn’t improve with a quick-relief inhaler
Conclusion
Asthma can be a manageable condition with the right treatment and awareness. By recognizing your triggers, taking prescribed medications, and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can lead a healthy and active life. Early diagnosis and consistent care are key to preventing asthma from disrupting your well-being.
Do you or someone you know struggle with asthma? Share your experience or tips in the comments below. Let’s support one another on the path to better breathing!