Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are one of the most common infections worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. While often mild, UTIs can become serious if left untreated, particularly when the infection spreads to the kidneys. Understanding what causes UTIs, the different types, signs and symptoms, risk factors, complications, and treatment options helps you recognize and manage this condition with confidence.
What Is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
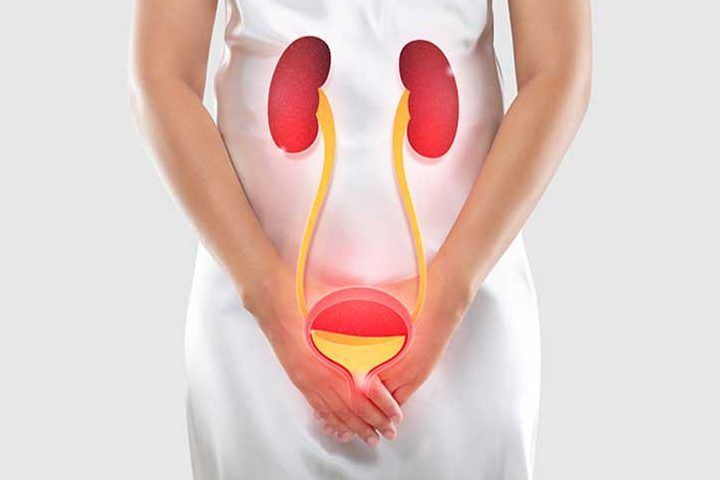
A Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) is an infection that occurs in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract, particularly the bladder and urethra. A UTI happens when bacteria enter the urinary tract, multiply, and cause inflammation and infection.
UTIs are especially common in women, with about half of all females experiencing at least one UTI during their lifetime. Men and children can also develop UTIs, although they are less common in these groups.
Anatomy of the Urinary Tract
Understanding the structure of the urinary tract helps explain how and where infections occur:
- Kidneys: Filter blood to remove waste and produce urine.
- Ureters: Carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: Stores urine before it is expelled.
- Urethra: The tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
Bacteria typically enter through the urethra and travel up into the bladder, causing the infection. If not treated, the bacteria can travel up to the kidneys, leading to more severe illness.
Types of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are classified based on which part of the urinary system is affected. While many people think of UTIs as a single condition, there are actually several distinct types, each with different causes, symptoms, risks, and treatment approaches. Understanding these types is essential for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and prevention of complications.
Understanding Down Syndrome: Causes, Types, Symptoms, & Treatment Options
According to the Mayo Clinic, UTIs can affect any part of the urinary tract, including the urethra, bladder, ureters, and kidneys, and the severity of infection generally increases as the infection moves upward toward the kidneys.
Why Understanding Types of UTI Matters
Each UTI type:
✔ Has different symptoms
✔ Requires specific diagnostic tests
✔ Needs tailored treatment
✔ Carries different risks of complications
Early recognition of the specific type of UTI improves outcomes and prevents kidney damage or systemic infection.
- Urethritis (Urethral Infection)
What Is Urethritis?
Urethritis is a UTI that affects the urethra, the narrow tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It is often the earliest point of entry for bacteria into the urinary system.
Urethritis can be caused by both urinary bacteria and sexually transmitted infections (STIs), making it distinct from other UTIs.
Common Causes Include:
- Bacterial entry from the skin or anus
- Sexually transmitted infections such as Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Irritation from soaps, spermicides, or urinary catheters
- Poor hygiene practices
Symptoms of Urethritis
Symptoms may vary by gender:
- Burning or pain during urination
- Itching or irritation at the urethral opening
- Discharge from the urethra (more common in men)
- Increased urinary urgency
- Mild pelvic discomfort
In women, urethritis symptoms may be subtle and sometimes mistaken for bladder infections.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause:
- Antibiotics for bacterial urethritis
- Targeted STI treatment if sexually transmitted
- Avoidance of irritants
Early treatment is important to prevent the infection from spreading upward into the bladder.
Thrombosis: Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Treatment
- Cystitis (Bladder Infection)
What Is Cystitis?
Cystitis is an infection of the bladder and is the most common type of UTI, especially in women. It occurs when bacteria travel up the urethra and multiply in the bladder.
Mmost cases of cystitis are caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), bacteria that normally live in the intestines.
Common Causes
- Improper wiping technique (back-to-front)
- Sexual activity
- Holding urine for long periods
- Incomplete bladder emptying
- Use of urinary catheters
- Pregnancy-related urinary changes
Symptoms of Cystitis
- Strong and persistent urge to urinate
- Burning sensation during urination
- Frequent urination with small urine volumes
- Cloudy, dark, or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Pelvic pressure or discomfort
Unlike kidney infections, cystitis usually does not cause fever unless it worsens.
Treatment
- Short-course oral antibiotics
- Increased fluid intake
- Pain relievers if needed
When treated promptly, cystitis typically resolves within a few days.
- Pyelonephritis (Kidney Infection)
What Is Pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis is a serious upper urinary tract infection involving one or both kidneys. It often occurs when a lower UTI spreads upward through the ureters to the kidneys.
Renal Failure: Causes, Symptoms, Types & Treatment Options
Kidney infections are considered medical emergencies due to the risk of permanent kidney damage and sepsis.
Common Causes
- Untreated or poorly treated bladder infections
- Urinary tract blockages (kidney stones, enlarged prostate)
- Structural abnormalities of the urinary tract
- Vesicoureteral reflux (backward flow of urine)
- Weakened immune system
Symptoms of Kidney Infection
- High fever (often above 38°C / 100.4°F)
- Chills and shaking
- Severe back, side, or flank pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue and weakness
- Confusion (especially in older adults)
These symptoms are often more severe than those of lower UTIs.
Treatment
- Immediate antibiotics, often intravenously
- Hospitalization in severe cases
- Follow-up imaging to rule out obstruction
Delayed treatment can lead to permanent kidney damage or bloodstream infection (sepsis).
- Ureteritis (Ureter Infection)
What Is Ureteritis?
Ureteritis is an infection of the ureters, the tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. It is relatively rare and usually occurs alongside kidney or bladder infections. Ureteritis often results from the spread of infection from other parts of the urinary tract rather than occurring on its own.
Symptoms
- Pain in the lower abdomen or flank
- Burning during urination
- Fever
- Symptoms similar to bladder or kidney infection
Treatment
- Antibiotics
- Treatment of the underlying infection
- Management of urinary obstruction if present
- Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
What Are Recurrent UTIs?
Recurrent UTIs occur when a person experiences:
- Two or more UTIs within six months, or
- Three or more UTIs within one year
Recurrent UTIs are especially common in women due to anatomical factors and hormonal changes.
Risk Factors for Recurrent UTIs
- Sexual activity
- Menopause
- Genetic susceptibility
- Incomplete bladder emptying
- Chronic catheter use
Management
- Preventive low-dose antibiotics
- Post-intercourse antibiotic therapy
- Behavioral and hygiene changes
- Addressing anatomical abnormalities
Neuralgia: Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Effective Treatments
- Complicated vs. Uncomplicated UTIs
Uncomplicated UTIs
- Occur in otherwise healthy individuals
- Typically limited to the bladder
- Respond well to standard antibiotic therapy
Complicated UTIs
- Occur in people with underlying health issues such as:
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Kidney disease
- Urinary tract abnormalities
- Require longer or stronger treatment
Complicated UTIs carry a higher risk of treatment failure and recurrence.
Causes of Urinary Tract Infections
UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply faster than the immune system can fight them off. The most common cause is the bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally lives in the intestine. When it travels from the bowel to the urethra and bladder, it can trigger infection.
Multiple Myeloma: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment Options
How Bacteria Enter the Urinary Tract
- Improper hygiene habits (e.g., wiping back to front).
- Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urethra.
- Urinary catheters used in hospitals can introduce bacteria directly.
- Incomplete bladder emptying, due to conditions like urinary retention or prostate enlargement.
- Blockages from stones or tumors that slow urine flow, allowing bacteria to grow.
- Suppressed immune system (due to diabetes, medication, or other illnesses).
- Congenital urinary tract abnormalities that facilitate bacterial spread.
These factors can increase the likelihood that bacteria will enter and persist in the urinary tract.
Risk Factors for UTIs
Certain groups are more prone to getting UTIs:
✔ Women: due to a shorter urethra which makes bacterial entry easier.
✔ Sexually active individuals: especially women after intercourse.
✔ Older adults: weakened immunity and incomplete bladder emptying increase risk.
✔ Pregnant women: hormonal and urinary changes elevate risk.
✔ Individuals with urinary catheters: medical devices that bypass natural defenses.
✔ People with diabetes: high sugar levels can weaken immune response and promote bacterial growth.
✔ Men with prostate enlargement: can trap urine and create bacterial breeding grounds.
✔ Constipation: increases bacteria exposure.
Common Symptoms of UTIs
UTI symptoms depend on the part of the urinary tract affected but they often share core features. Common symptoms include:
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (Bladder & Urethra) Symptoms
- Burning sensation during urination (dysuria)
- Strong, frequent urge to urinate
- Passing small amounts of urine
- Cloudy, strong-smelling urine
- Pelvic discomfort or pressure
- Blood in urine (hematuria)
Kidney (Upper UTI) Symptoms
- High fever
- Chills or shaking
- Pain in the back or side (below ribs)
- Nausea and vomiting
- General malaise or feeling unwell
In older adults, UTIs may present with non-specific symptoms such as confusion, sudden change in behavior, or fatigue rather than classic urinary symptoms. ([turn0search1]; [turn0search3])
Diagnosis of a UTI
If you suspect a UTI, healthcare providers typically use the following tests to confirm the infection and guide treatment:
- Urinalysis: A urine sample is checked for white blood cells, red blood cells, bacteria, or other signs of infection.
- Urine Culture: Lab technicians grow bacteria from the urine sample to identify the specific organism and determine which antibiotic is most effective.
- Imaging or Cystoscopy: For recurrent UTIs or complicated cases, imaging (ultrasound, CT scan) may be used. A cystoscopy using a thin camera to inspect the bladder may also be recommended.
Treatment Options for UTIs
- Antibiotics
Antibiotic therapy is the primary treatment for most UTIs, tailored to the bacteria identified in the urine culture and the patient’s health status. The specific antibiotic and duration depend on the UTI type and severity.
Common antibiotics from Mayo Clinic’s UTI treatment include:
- Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
- Nitrofurantoin
- Fosfomycin
- Cephalexin
- Ceftriaxone
For severe infections especially when the infection has reached the kidneys, intravenous (IV) antibiotics and hospitalization may be necessary.
- Supportive Care
In addition to antibiotics, doctors often recommend:
- Drinking plenty of fluids to help flush out bacteria.
- Pain relievers for discomfort.
- Heat therapy (a warm compress for abdominal pain).
- Avoiding bladder irritants (such as caffeine or alcohol).
- Preventive Antibiotic Strategies
For people with frequent UTIs, doctors may:
- Prescribe low-dose antibiotics over longer periods.
- Provide a single antibiotic dose after sex if UTIs are related to sexual activity.
- Recommend self-start antibiotic therapy at the first sign of symptoms.
- Non-Antibiotic Approaches
Although antibiotics are essential for treating active UTIs, some preventive strategies may help reduce recurrence:
- Hydration and regular urination
- Proper genital hygiene
- Cranberry products (juice or supplements) may reduce recurrent infections, though evidence is mixed, notes by Verywell Health
Complications of Untreated UTIs
When treated promptly, UTIs rarely cause long-term problems. However, untreated or poorly managed UTIs can lead to serious complications such as:
✔ Kidney damage: Infection spreading to the kidneys (pyelonephritis) can cause permanent scarring and loss of function.
✔ Sepsis: A life-threatening spread of infection into the bloodstream, especially in older adults or people with weakened immune systems.
✔ Recurring infections: UTIs that keep returning may increase the risk of chronic problems.
✔ Prostate involvement in men: Repeated UTIs can lead to prostatitis or urethral scarring.
Because UTIs can escalate quickly, early diagnosis and treatment are key.
Prevention Strategies
Although not all UTIs are preventable, you can take steps to reduce the risk of being infected:
✔ Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water flushes bacteria from the urinary tract before they can cause infection.
✔ Practice Good Hygiene: Wipe front to back, especially for women, to prevent bacterial transfer from the rectum to the urethra.
✔ Urinate Often: Don’t hold urine for long periods, regular bladder emptying flushes out bacteria.
✔ Urinate After Sex: Flushing bacteria introduced during intercourse can help prevent infection.
✔ Avoid Irritants: Perfumed products in the genital area can irritate urethral tissue and increase susceptibility.
✔ Proper Birth Control Choices: Certain methods like diaphragms or spermicides can increase UTI risk. Talk to your clinician if you notice repeated infections.
When to See a Healthcare Provider
Seek medical advice if you experience:
- Painful or frequent urination
- Blood in your urine
- Fever, chills, or flank pain
- Symptoms that last more than 24–48 hours
- Recurring UTIs despite treatment
For infants, older adults, pregnant women, or people with weakened immune systems, even mild symptoms deserve prompt evaluation.
Most UTIs respond well to antibiotics, and symptoms often improve within a few days of starting treatment. However, completing the full antibiotic course is critical even if symptoms stop to prevent recurrence and resistance.
Talk to your healthcare provider about preventive strategies if UTIs occur frequently. Some people benefit from lifestyle changes, targeted supplements, or medically guided preventive antibiotic use under supervision.